Quick Start Guide
New to AI coding? Start here:
- Install Cursor (free tier available)
- Use GPT-5.1 for fast tasks, Claude Opus 4.5 for complex refactoring
- Learn the CRISP prompt framework
- Review all AI-generated code before committing
Already using AI tools? Jump to:
I recently refactored an authentication system in 45 minutes that would have taken 4 hours manually. The AI handled 8 files simultaneously, updated tests, and caught edge cases I would have missed. This isn’t autocomplete - it’s autonomous coding.
In 2026, AI development tools have evolved from simple tab completion to agents that reason through problems, execute multi-file changes, and iterate on their own output. The question isn’t whether to use AI for coding - it’s which tools match your workflow and how to use them without introducing more bugs than they fix.
TL;DR: AI-Augmented Development in 2026
- Best multi-file editor: Cursor - Composer mode, 8 parallel agents, RAG-optimized codebase awareness
- Best autonomous: AWS Kiro - Persistent multi-repo orchestration (9/10 autonomy)
- Best free tier: Google Antigravity - 5 parallel agents, access to Claude 4.5
- Best value: Windsurf - $15/mo for solid agentic flow
- Best coding models: Claude Opus 4.5 (80.9%) and GPT-5.2 (80%) lead on SWE-bench
- Best speed-to-quality: Gemini 3 Flash (78% SWE-bench, fastest inference)
- Largest context window: Gemini 3 Pro (1M tokens for large codebase analysis)
- Reality check: AI is a multiplier, not a replacement. Human supervision is required for architecture, security, and verifying stochastic outputs.
 Figure 1: The 2026 AI Editor Decision Tree - Which tool fits your project stack?
Figure 1: The 2026 AI Editor Decision Tree - Which tool fits your project stack?
Part 1: AI Code Editors & IDEs
Cursor is an AI-first code editor forked from VS Code with agent mode for high-level goal execution. It uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide deep context-awareness, making it my go-to recommendation for codebase-wide refactoring.
Key Features (2026):
- Composer 2.0: Multi-file editing with parallel agents using Git worktrees
- RAG-Powered Context: Uses @References (@file, @Codebase) to pull the most relevant functions into the prompt window, optimizing token efficiency.
- BugBot: Automated PR reviewer with 1-click fixes
- YOLO Mode: Maximum autonomy for trusted codebases
My Experience:
Cursor has doubled my productivity for multi-file refactoring. The Composer mode alone is worth $20/mo - I use it daily for feature implementations that touch 5-10 files. That said, it’s not for beginners. You need to know what you’re prompting for, or you’ll get hallucinations that waste more time than they save.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Best multi-file editing | $20/mo (vs $10 Copilot) |
| Deep codebase awareness | Resource-heavy on large projects |
| Parallel agents | Learning curve for prompting |
| Model flexibility | Still needs code review |
Windsurf by Codeium is an AI-native IDE optimized for developer flow. Its Cascade agent manages multi-file reasoning by building a project-wide context map that detects proactive issues before you even type.
Key Features:
- Cascade Agent: Plans, edits, and self-iterates until the terminal command passes.
- Turbo Mode: Executes tasks with high autonomy, often resolving bugs in one pass.
- Local-First Memories: Remembers codebase patterns locally to ensure privacy and low-latency suggestions.
- MCP Integrations: Connects to GitHub, Slack, and Stripe to pull external data into the reasoning loop.
My Experience:
Windsurf’s Cascade thinks like an agent, not just autocomplete - it’s excellent for navigating large monorepos. However, I’ve noticed quality declined in late 2025. The AI sometimes produces nonsensical responses that it didn’t before. I’m hopeful this is temporary as they iterate.
| Mode | Autonomy | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Chat Mode | Low | Explanations, debugging |
| Write Mode | Medium | Controlled generation |
| Turbo Mode | High | Full features, refactoring |
Kiro presents a shift from stochastic (random) code generation to deterministic development. By generating structured specifications before writing a single line of code, Kiro ensures that the AI’s output adheres to your architectural constraints every time.
Key Features:
- Spec-Driven Architecture: Replaces “guessing” with verification. The AI generates a blueprint, asks for approval, then executes.
- Multi-Repo Persistence: Can handle 15+ repositories in a single agent session, perfect for microservices.
- AWS Native Hooking: Direct integration with Bedrock ensures your data never leaves your enterprise VPC.
- Variable Precision: Uses Claude Haiku 4.5 for fast tasks and Claude Opus 4.5 for high-reasoning “Thinking” sessions.
My Experience:
Kiro’s planning mode is a significant leap forward in autonomous coding. In my testing, its ability to maintain state across multi-day tasks and orchestrate changes across 15+ repositories simultaneously is unmatched. Unlike editors that require constant “vibe” checks, Kiro follows its generated specs with high precision. It’s the only tool I’ve seen that can truly be left alone to build out entire backend infrastructures while you sleep.
GitHub Copilot: Universal IDE Support
GitHub Copilot remains the most widely adopted assistant with universal IDE support - VS Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains, Vim, and Neovim.
Key Features:
- Copilot Chat: Integrated conversational AI
- Copilot Workspace (Beta): Plan features from natural language
- Enterprise Security: IP indemnification, data privacy
- Widest IDE Support: Works everywhere
Best For: Teams that can’t switch IDEs, enterprise compliance requirements, or developers who want simple completions without learning new tools.
Google Antigravity is the agent-first IDE from Google DeepMind. It is currently the only tool providing high-end LLM power (Gemini 3 Pro) for free, making it the premier choice for developers optimizing for token efficiency.
Key Features:
- Mission Control Coordination: Orchestrates 5 specialized agents working on different layers of your stack simultaneously.
- Multimodal Validation: The Browser Agent doesn’t just check code; it “looks” at your UI to verify design-to-code fidelity.
- Zero-Credit Completions: Basic tab completions are handled by local models, reserving cloud power for complex reasoning.
My Experience:
Antigravity is the most ambitious agent-first approach I’ve tested. The free tier is remarkably generous - accessing Claude Opus 4.5 and Gemini 3 Pro at no cost. The learning curve is steep, but the ceiling for autonomous coding is higher than Cursor or Windsurf. Worth trying for greenfield projects.
Quick Comparison: AI Code Editors
| Feature | Cursor | Windsurf | Antigravity | Kiro | Copilot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | ✅ Solid | ⚠️ Variable | ⚠️ New | ✅ Engineering Grade | ✅ Solid |
| Autonomous tasks | ✅ Agent | ✅ Turbo | ✅ Native | ✅ Industry Lead | ⚠️ Workspace |
| IDE support | VS Code fork | VS Code fork | Standalone | VS Code fork | All major |
AI Code Editor Pricing (2026)
| Tool | Free Tier | Pro Tier | Enterprise/Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cursor | 2000 code completions | $20 (Unlimited tab) | $200 (20x usage) |
| Windsurf | 25 prompt credits | $15 (500 credits) | $30/user (Teams) |
| Kiro | 50 credits (No Opus) | $20 (1,000 credits) | $200 (10,000 credits) |
| Antigravity | Public Preview (Free) | Incl. Google One | Incl. Workspace AI |
| Copilot | N/A | $10/mo | $39/user (Enterprise) |
Feature Comparison by Pricing Tier
| Price Point | Best Value | What You Get |
|---|---|---|
| Free | Antigravity | 5 parallel agents, Claude 4.5, Gemini 3 Pro |
| $10-15/mo | Windsurf ($15) | 500 credits, Cascade agent, solid autonomy |
| $20/mo | Cursor | Unlimited completions, 8 parallel agents, best stability |
| Enterprise | Kiro ($200) | 10,000 credits, multi-repo orchestration, AWS integration |
Autonomous Coding Agent Ratings (2026)
Note: These ratings reflect my personal experience testing these tools in production environments. Your results may vary based on project complexity and workflow.
| Tool | Autonomy Rating | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kiro | 9/10 | Persistent operation, multi-repo, specs | Standalone platform, steeper curve |
| Cursor Agent | 8.5/10 | Long-running projects, browser build | Privacy concerns, more check-ins |
| Antigravity | 8/10 | 5 parallel agents, mission control | Session-based, merge conflicts |
| Windsurf Cascade | 7/10 | IDE-native, proactive, great UI | Slower execution, shorter sessions |
Part 2: Understanding the Core Technology
To use AI coding tools effectively, you need to understand the underlying technology that allows them to “know” your 100,000-line codebase.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
When you ask Cursor or Windsurf about your codebase, they don’t send the entire source to the LLM - that would be prohibitively expensive and slow. Instead, they use RAG:
- Indexing: Your code is converted into mathematical vectors (embeddings)
- Retrieval: When you prompt, the system finds code semantically “closest” to your intent
- Augmentation: Only relevant snippets are injected into the prompt
Why this matters: If your AI is hallucinating, it’s usually a retrieval failure. Fix this by explicitly @-referring to the file the AI is missing.
Example:
❌ "Update the auth logic"
✅ "Update the auth logic in @auth-service.ts and @middleware/auth.ts"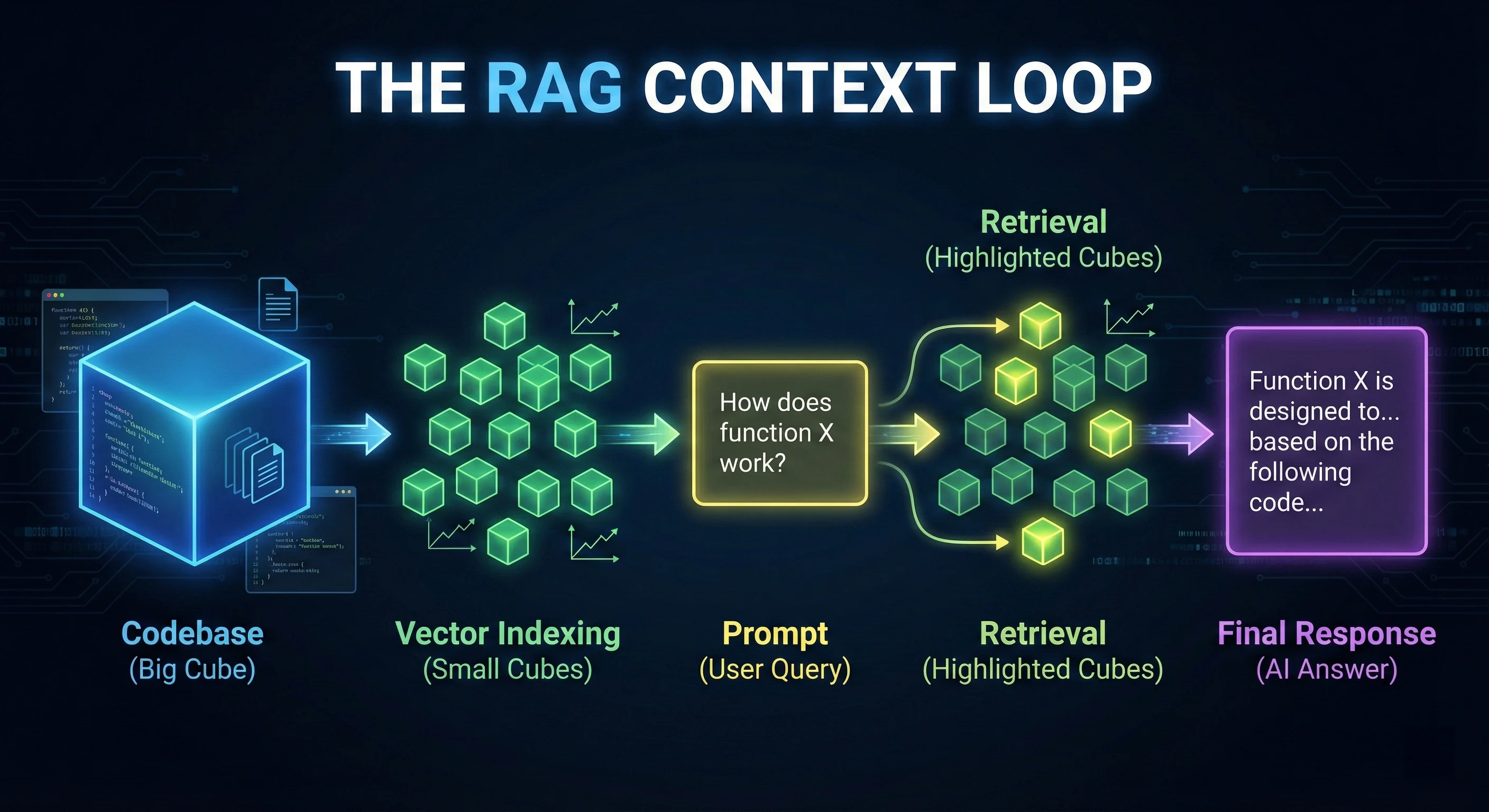 Figure 2: The RAG Context Loop - How agentic IDEs index and retrieve your codebase context.
Figure 2: The RAG Context Loop - How agentic IDEs index and retrieve your codebase context.
Context Windows: Why Size Matters
Modern models like Claude Opus 4.5 offer 200K+ context windows. This allows the AI to “hold” much larger architectural patterns in active memory than previous generations.
Context window = the amount of text (measured in tokens) a model can process at once. Larger windows enable better understanding of complex codebases.
| Model | Context Window | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o | 128K tokens | Component-level refactoring |
| Claude Opus 4.5 | 200K tokens (1M beta) | System-level architecture |
| GPT-5.2 | 400K tokens | Multi-repo orchestration |
| Gemini 3 Pro | 1M tokens | Entire codebase analysis |
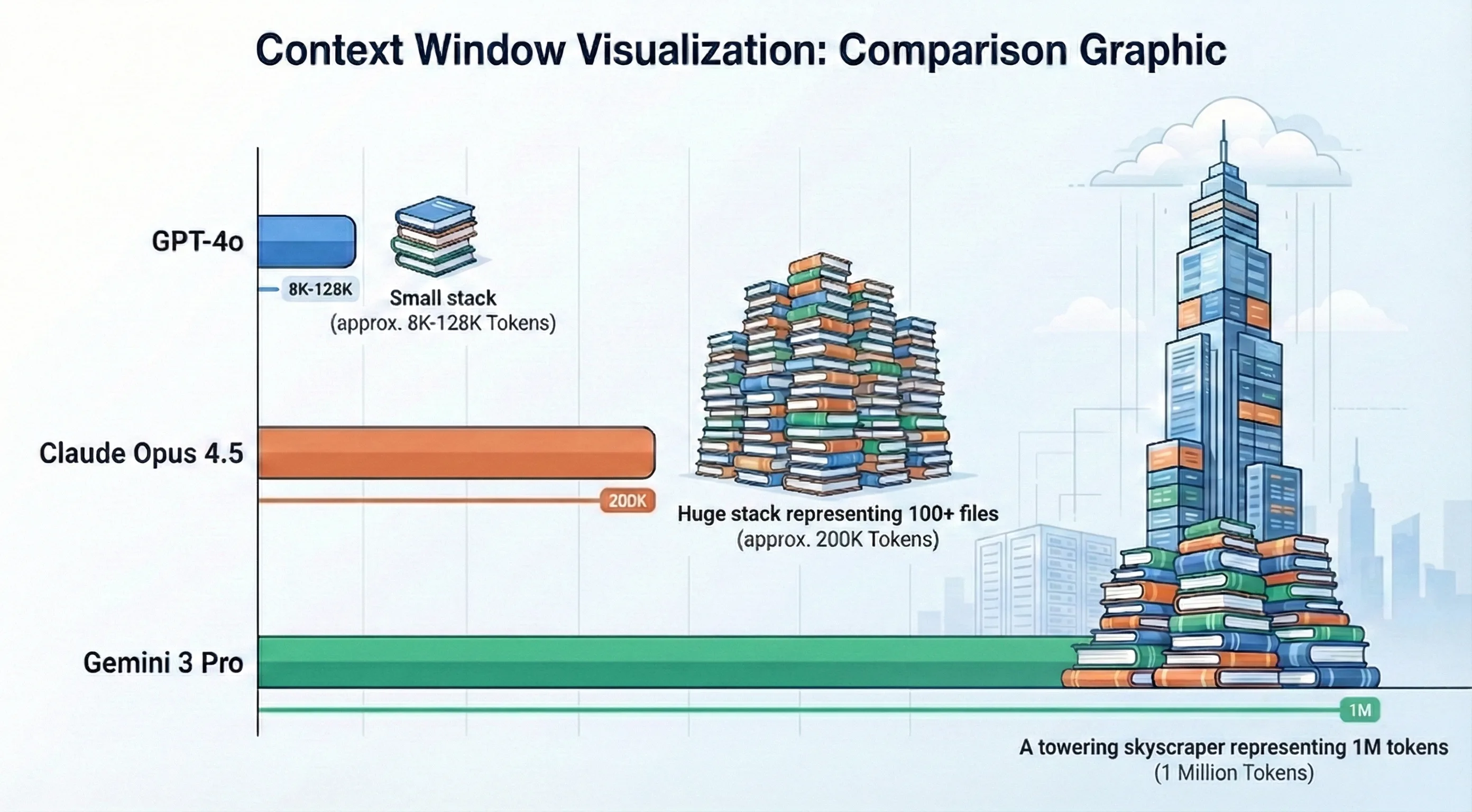 Figure 3: Context Window Comparison - Visualizing the reasoning capacity of 2026 LLMs.
Figure 3: Context Window Comparison - Visualizing the reasoning capacity of 2026 LLMs.
Local-First Inference and Privacy
For enterprise teams with strict data policies, cloud LLMs are often a dealbreaker. Tools like Continue and Tabby allow you to run models locally using Ollama or Llama.cpp.
Benefits:
- Privacy: Your code never leaves your local machine or private network
- Latency: Zero network latency (though performance depends on your GPU)
- Cost: Unlimited tokens for the price of electricity
Requirements:
- M3 Max or RTX 4090 recommended for acceptable performance
- 32GB+ RAM for larger models
- Expect 30-50% lower quality vs. cloud models
Stochasticity vs. Determinism
LLMs are stochastic - they predict the next token based on probability, which leads to hallucinations. This is why the same prompt can produce different outputs.
Stochastic = random/probabilistic. Each time you run the same prompt, you may get slightly different code.
Kiro’s solution: Force a deterministic spec first. You verify the logic chain before code is written, reducing output randomness.
Part 3: Latest LLM Models for Coding
GPT-5 Series (OpenAI)
The GPT-5 family launched in August 2025 with point releases in November (5.1) and December (5.2).
GPT-5.2 (December 2025):
- Context Window: 400K tokens
- SWE-bench Verified: 80%
- Adaptive Modes: “Instant” for simple queries, “Thinking” for complex workflows
- Best For: Multi-step agentic tasks, complex refactoring
- Trade-off: Slower on simple tasks due to thorough reasoning
GPT-5.1 (November 2025):
- Context Window: 400K tokens
- SWE-bench Verified: 76.3%
- Best For: Interactive pair programming, speed-critical tasks
- Key Improvement: Better formatting, full compilable files
Claude 4.5 Series (Anthropic)
Anthropic’s Claude 4.5 series represents their most capable models for coding.
Claude Opus 4.5 (November 2025):
- Context Window: 200K tokens (1M beta available)
- Best For: Long-form content, sensitive code, architectural planning
- Strength: Superior multi-file reasoning, safest behavior
- Powers: Claude Code CLI
Claude Sonnet 4.5:
- Best For: Daily coding tasks, agents
- Strength: Speed-quality balance
Claude Code CLI:
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
claude-code "Refactor the auth module to use JWT tokens.
Update all affected tests and regenerate API docs."Claude Code reads files, runs commands, edits code, and iterates autonomously in your terminal.
Gemini 3 Series (Google)
Launched November 2025, Gemini 3 powers Google Antigravity IDE.
| Model | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Gemini 3 Pro | Complex tasks, multimodal | Extended thinking toggle |
| Gemini 3 Flash | Speed-critical tasks | Fastest inference |
| Gemini 3 Deep Think | Algorithmic problems | Mathematical reasoning |
Best For: Google Workspace integration, multimodal workflows (images → code), video-to-code generation.
Understanding Benchmarks
SWE-bench Verified is the industry-standard benchmark for measuring how well AI models solve real-world GitHub issues. It tests models on 500 verified software engineering problems from popular open-source repositories. A score of 80% means the model successfully resolved 400 out of 500 real bugs without human intervention.
LLM Comparison for Coding
| Model | SWE-bench | Context | Best For | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claude Opus 4.5 | 80.9% | 200K (1M beta) | Best reasoning, sensitive code | Slow |
| GPT-5.2 | 80% | 400K | Adaptive reasoning modes | Medium |
| Gemini 3 Flash | 78% | 1M | Best speed-to-quality ratio | Very Fast |
| GPT-5.1 | 76.3% | 400K | Fast pair programming | Fast |
| Gemini 3 Pro | 76.2% | 1M | Google ecosystem, multimodal | Medium |
| Claude Sonnet 4.5 | 70.5% | 200K | Daily coding, agents | Fast |
Part 4: No-Code/Low-Code AI Builders
No-code builders let you generate full applications from natural language prompts. They’re ideal for MVPs, prototypes, and validating ideas before investing in custom development.
v0 by Vercel: Best for UI Generation
v0 is a collaborative AI assistant for building agents, apps, and websites with design mode, GitHub sync, and one-click Vercel deployment.
Key Features:
- UI Generation: React + Next.js + Tailwind + shadcn/ui from prompts or images
- Design Mode: Visual iteration on generated components
- Agentic by Default: Automatic database and API integration
- iOS App: Mobile development support
Best For: Rapid UI scaffolding, marketing sites, dashboards, component libraries.
Limitation: Frontend-focused - lacks built-in backend/database.
Lovable: Fastest Full-Stack MVPs
Lovable generates full-stack web apps with React, Tailwind, and Supabase from natural language. Creates complete front-end, backend, and database in one step.
Key Features:
- Full-Stack: React + TypeScript + Tailwind + Vite + Supabase backend
- Speed: MVP in as little as 12 minutes
- Editable Code: Real code synced to GitHub
- Multiplayer: Collaborative development in v2
My Experience:
Lovable delivers better default design quality than Bolt.new - the generated UIs look more polished out of the box. The trade-off is that it burns credits fast for complex requests, and manual cleanup is often needed for production use.
Best For: Non-technical founders, quick demos, landing pages with backend.
Bolt.new: Browser-Based Full-Stack
Bolt.new is a browser-based full-stack app generator with zero setup required.
Key Features:
- Browser IDE: No local setup
- Framework Agnostic: React, Vue, Next.js, Astro, Svelte, React Native (Expo)
- Full-Stack: Frontend + backend + database from prompts
- Code Export: Download or sync to GitHub
My Experience:
Excellent for quick frontend prototypes, and the code export gives you real control over the output. One frustration: the AI sometimes keeps adding back code I’ve removed, which burns tokens. For complex iterations, costs can pile up quickly.
Best For: Quick prototyping, testing ideas, browser-based development.
Replit: Full Cloud IDE
Replit is best for rapid prototyping and cloud development with full control, AI integration via Ghostwriter/Replit Agent, and team collaboration.
When to Use Replit over Lovable/Bolt.new:
- Need production-grade versioning and stability
- Complex backend logic beyond Supabase
- Team scalability requirements
- 50+ programming language support
My Recommendation:
Use Lovable for validating ideas quickly. Switch to Replit when you need real infrastructure and long-term maintenance. The no-code builders are excellent for MVPs but struggle with production-grade complexity.
Anything: Mobile App Builder
Anything is an AI agent-powered builder for sites, apps, and products supporting iOS/Android with one-click App Store deployment.
Key Features:
- Mobile Native: Build iOS and Android apps from natural language
- Large Projects: Automatic refactoring for projects >100k lines of code
- One-Click Deploy: Ship to App Store and web instantly
- Error Detection: Automatically detects and fixes errors
- Asset Generation: Creates images, icons, and assets
Best For: Mobile apps, cross-platform products, founders who need App Store presence.
Limitation: Newer platform - less community resources than established tools.
Base44: SaaS Builder with Payments
Base44 generates full SaaS applications with built-in backend, database, payments, and authentication from natural language prompts.
Key Features:
- Full SaaS Stack: Frontend + backend + database + auth + Stripe payments
- Instant Hosting: Apps deployed and hosted immediately
- Integrations: Gmail, Slack, Stripe, Google Calendar, any API
- White-Label: Custom branding, domains, typography
- Chat Refinement: Iterate on your app through conversation
Pricing (2026):
- Free: $0/mo - 25 message credits, 100 integration credits
- Starter: $16/mo (billed annually) - 100 message credits, 2,000 integration credits
- Builder: $40/mo (billed annually) - 250 message credits, 10,000 integration credits
- Pro: $80/mo (billed annually) - 500 message credits, 20,000 integration credits
- Elite: $160/mo (billed annually) - 1,200 message credits, 50,000 integration credits
Best For: SaaS MVPs, internal tools, apps needing payments/auth out of the box.
No-Code Builder Comparison
| Feature | v0 | Lovable | Bolt.new | Anything | Base44 | Replit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | UI components | Full-stack MVP | Prototypes | Mobile apps | SaaS apps | Production |
| Mobile | ❌ | ❌ | ⚠️ Expo | ✅ Native | ❌ | ⚠️ |
| Backend | ❌ | ✅ Supabase | ✅ Basic | ✅ | ✅ Built-in | ✅ Full |
| Payments | ❌ | ✅ Stripe | ❌ | ✅ Stripe | ✅ Stripe | ⚠️ Manual |
| Large Projects | ⚠️ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ 100k+ LOC | ⚠️ | ✅ |
| Non-Dev Friendly | ✅ | ✅ Best | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
Part 5: Specialized AI Tools
Devin: Autonomous AI Software Engineer
Devin by Cognition Labs is positioned as the first autonomous AI software engineer, handling entire projects from planning through deployment.
Reality Check (January 2026 Assessment):
- Independent testing shows ~15% success rate on complex tasks (3 out of 20 in one study)
- Official SWE-bench: 13.86% unassisted resolution rate
- Struggles with vague or complex instructions requiring architectural decisions
- Excels at repetitive tasks: migrations, refactoring, bug fixing
- Nubank case study: 12x efficiency on ETL migration
- By late 2025: 67% PR merge rate (up from 34%), 4x faster on defined tasks
Cost: ~$500/month for team tier
Open-Source Alternatives
For privacy, customization, and cost control:
| Tool | Type | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Aider | Terminal pair programmer | Git integration, multi-file editing |
| Continue | IDE extension | Model flexibility, local LLMs |
| Tabnine | Enterprise completions | Privacy-focused, on-premise |
| Tabby | Self-hosted assistant | Full privacy, customization |
AI Code Review Tools
Beyond code generation, AI is transforming the PR review process. These tools integrate with GitHub to provide automated, context-aware code reviews.
CodeRabbit
CodeRabbit provides automated PR reviews with line-by-line suggestions, security vulnerability detection, and interactive chat.
Key Features:
- Continuous Reviews: Incremental review on each commit
- Context-Aware: Uses code graph analysis to understand the full repo
- Blazing Fast: Results typically within 5 seconds
- 35+ Linters: Integrates static analysis tools
- MCP Integration: Pulls context from docs and project management tools
My Experience:
CodeRabbit catches issues I’d miss in manual review - especially security vulnerabilities and logic flaws across files. The 5-second response time means I get feedback before I’ve even finished the PR description. In my workflow, it’s proven worth integrating into serious team processes.
Greptile
Greptile builds a “codebase knowledge graph” to provide deep, institutional understanding of your project.
Key Features:
- Knowledge Graph: Maps function calls, class inheritance, module dependencies
- 3x Bug Detection: Benchmarks show higher catch rates than competitors
- Jira/Notion Integration: Understands context behind code changes
- AI Staff Engineer: Acts like an experienced team member who knows the codebase
My Experience:
Greptile is the most “intelligent” reviewer I’ve tested - it catches issues that require understanding how the codebase fits together. The Jira integration is particularly useful in my workflow for ensuring PRs match ticket requirements.
Cursor AI Features
Cursor provides built-in code review and debugging capabilities for paid users.
Key Features:
- Diff Analysis: Reviews code changes using Cursor’s AI models
- 1-Click Fixes: Apply suggested fixes directly in Cursor
- Customizable: Run on all PRs, only when mentioned, or manually
- Free for Paid Users: Included with Cursor Pro/Pro+/Ultra
My Experience:
If you’re already using Cursor, BugBot is a no-brainer - it’s integrated into your workflow. The 1-click fixes are convenient for quick iterations in my testing. However, for teams not on Cursor, CodeRabbit or Greptile offer more flexibility.
Code Review Tools Comparison
| Feature | CodeRabbit | Greptile | Cursor BugBot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Fast PR reviews | Deep codebase understanding | Cursor users |
| Speed | ✅ ~5 seconds | ⚠️ Slower (deeper analysis) | ✅ Fast |
| Codebase Context | ✅ Good | ✅ Best (knowledge graph) | ⚠️ Diff-focused |
| Integrations | ✅ GitHub, GitLab, MCP | ✅ GitHub, Jira, Notion | ⚠️ GitHub only |
| Price | Free tier + paid | Free tier + paid | Included with Cursor |
Part 6: The CRISP Prompt Engineering Framework
Effective prompts are the difference between AI that helps and AI that wastes time. The CRISP framework provides a structured approach to communicating with AI coding assistants.
CRISP Components
- Context: Share relevant files, error messages, constraints
- Role: Tell AI what perspective to take
- Intent: What are you trying to accomplish?
- Specifics: Tech stack, patterns, naming conventions
- Preferences: Style, error handling, edge cases
Real-World CRISP Examples
Example 1: Component Creation
❌ Vague prompt:
Create a table component✅ CRISP prompt:
Context: React 19 app using @components/ui/Button.tsx patterns
Role: Senior React developer valuing accessibility and performance
Intent: Create a sortable data table for user records with pagination
Specifics: TypeScript generics, TanStack Table v9, design tokens from @tokens.css
Preferences: Keyboard navigation, ARIA labels, virtualization for 1000+ rowsExample 2: Authentication Refactoring
❌ Vague prompt:
Fix the auth system✅ CRISP prompt:
Context: @auth-module.ts currently uses JWT in localStorage (security risk)
Role: Senior Security Engineer
Intent: Migrate to HTTP-only cookies with refresh token rotation
Specifics: Node.js 22, Express 5.0, Redis for token storage, 15min access / 7day refresh
Preferences: Include middleware tests, update Swagger docs, add rate limitingExample 3: Performance Optimization
❌ Vague prompt:
Make this faster✅ CRISP prompt:
Context: @UserDashboard.tsx renders 500+ items, causing 3s load time
Role: Performance engineer focused on Core Web Vitals
Intent: Reduce initial render to <1s while maintaining UX
Specifics: React 19, already using React.memo, need virtualization
Preferences: Use react-window, lazy load images, maintain scroll positionPart 7: MCP - Model Context Protocol
MCP is what separates good AI workflows from great ones. It lets AI assistants connect to external data sources beyond the files you paste.
Supported By
- Cursor ✅
- Kiro ✅
- Claude Desktop ✅
- Windsurf (limited)
Available MCP Servers
| MCP Server | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Figma | Design-to-code workflows |
| PostgreSQL | Database schema context |
| GitHub | Issue and PR context |
| Slack | Team discussion context |
| Stripe | Payment API context |
The Figma MCP integration is particularly powerful for design engineers who need to maintain consistency between design systems and code implementations.
Setting Up Figma MCP
npm install -g @anthropic/mcp-server-figmaConfigure Claude Desktop (~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json):
{
"mcpServers": {
"figma": {
"command": "mcp-server-figma",
"env": {
"FIGMA_ACCESS_TOKEN": "your-token"
}
}
}
}Part 8: Common Pitfalls
Based on common developer frustrations I’ve observed:
Pitfall 1: Accepting Without Reviewing
AI-generated code often looks correct but misses critical details. Always review for security, error handling, and edge cases.
Example: Form Submission
// ❌ AI generated - missing auth, error handling, headers
const handleSubmit = async (data: FormData) => {
await fetch('/api/users', { method: 'POST', body: JSON.stringify(data) });
};
// ✅ After review - added auth, error handling, proper headers
const handleSubmit = async (data: FormData) => {
const response = await fetch('/api/users', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': `Bearer ${token}`
},
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Failed to create user: ${response.statusText}`);
}
return response.json();
};Example: Database Query
// ❌ AI generated - SQL injection vulnerability
const getUser = async (userId: string) => {
return db.query(`SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ${userId}`);
};
// ✅ After review - parameterized query prevents SQL injection
const getUser = async (userId: string) => {
return db.query('SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = $1', [userId]);
};Security vulnerabilities like SQL injection are common in AI-generated code. Using TypeScript with proper type definitions helps catch many of these issues at compile time, but manual security review is still essential.
Example: React Component
// ❌ AI generated - missing accessibility, key prop, loading state
const UserList = ({ users }) => (
<ul>
{users.map(user => <li>{user.name}</li>)}
</ul>
);
// ✅ After review - added accessibility, keys, loading/error states
const UserList = ({ users, loading, error }) => {
if (loading) return <div role="status">Loading users...</div>;
if (error) return <div role="alert">Error: {error.message}</div>;
if (!users.length) return <p>No users found</p>;
return (
<ul aria-label="User list">
{users.map(user => (
<li key={user.id}>{user.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
};AI-generated components often miss critical accessibility patterns and proper error handling. Always verify ARIA attributes, keyboard navigation, and loading states before shipping to production.
Pitfall 2: Wrong Tool for the Job
| Task | Wrong Tool | Right Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Simple autocomplete | Claude Opus 4.5 (expensive) | Gemini 3 Flash, Copilot |
| Multi-file refactor | ChatGPT (no codebase context) | Cursor Composer |
| UI prototype | Cursor (overkill) | v0, Lovable |
| Production app | Lovable (limited) | Replit, Cursor |
Choosing the right tool significantly impacts productivity. For React applications, understanding modern state management patterns helps you architect AI-generated code that scales properly from prototype to production.
Pitfall 3: Expecting Too Much from “Autonomous” Tools
Devin is marketed as autonomous, but my testing confirms it often struggles with tasks requiring deep architectural context, completing roughly 15% of complex requests without intervention. It still needs heavy supervision.
All AI tools require:
- Clear, specific prompts
- Human review of output
- Architecture decisions by humans
- Security verification
Part 9: The Future: Vibe Coding & Agentic Autonomy
As we move through 2026, the term “Coding” is being replaced by “Vibe Coding.” This isn’t just a meme; it represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with machines.
From Autocomplete to Intent
We are moving away from writing lines of code and toward describing intent. The AI isn’t just suggesting the next word; it’s suggesting the next architecture. Tools like Antigravity and Claude Code are the vanguard of this movement, where the “Developer” becomes more of a “Systems Orchestrator.”
The Multi-Agent Future
In 2025, we got used to one AI assistant. In 2026, we are managing teams of agents. Cursor’s Composer already supports 8 parallel agents. By the end of this year, expect your IDE to spawn specialized agents for testing, security, and documentation that run in the background while you focus on the “vibe” and high-level logic.
Advice for the Modern Developer
Don’t fear the agents. Instead, master the spec. The developers who thrive in 2026 are those who can clearly define requirements, verify AI output with precision, and understand the underlying systems well enough to fix the 15% that the AI gets wrong.
Key Takeaways
- Cursor leads for daily workflow - RAG-optimized Composer mode handles 90% of multi-file tasks with parallel agent support
- Kiro excels at autonomy - Spec-driven architecture enables complex, multi-repo infrastructure work with minimal supervision
- Antigravity offers best value - Generous free tier with parallel agents and access to top models (Claude 4.5, Gemini 3 Pro)
- Claude Opus 4.5 leads benchmarks - 80.9% SWE-bench score with 200K context window for superior reasoning on complex tasks
- Prompting is the new skill - CRISP framework mastery differentiates effective orchestration from frustrating hallucinations
- AI review catches more bugs - CodeRabbit and Greptile detect 30% more logic errors than manual review alone
- Local LLMs ensure privacy - Continue + Ollama provides enterprise compliance without sacrificing development speed
- Always review AI output - Current tools require human verification for security, architecture, and edge cases
Related Resources
- The Design Engineer’s Guide - How to bridge designs to code with AI.
- TypeScript Patterns - Why strong types prevent 40% of AI hallucinations.
- React Performance Optimization - Using AI to identify rerender bottlenecks.

